
Accounts receivable is a current asset that results when a company reports revenues from sales of products or the providing of services on credit using the accrual basis of accounting. The effect on the company’s balance sheet is an increase in current assets and an increase in owner’s or stockholders’ equity. The company’s income statement will also report the amount of the revenues earned. With this method, accounts receivable is organized into categories by length of time outstanding, and an uncollectible percentage is assigned to each category.
Accounting Journal Template
- So, if accounts receivable doesn’t appear on the income statement, where does it appear on the balance sheet?
- This variance in treatment addresses taxpayers’ potential to manipulate when a bad debt is recognized.
- The estimation is typically based on credit sales only, not total sales (which include cash sales).
- These cases are not rare and usually, involve bad debts or allowance for doubtful debts.
- One way to get people to pay you sooner is to make it worth their while.
- Then all of the category estimates are added together to get one total estimated uncollectible balance for the period.
Companies record these amounts as expenses, which become a part of the income statement. Usually, bad debts are prevalent for companies that provide credit sales. As mentioned above, accounts receivable represents money owed by customers. When the customers repay the company, it will result in monetary income. While the company may have recorded the related revenues bookkeeping already, the receipt will only decrease the balance.
Frequently Asked Questions About The Differences Between Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable
Using this accounts payable template will help to keep track of what you owe to each party, and will provide a quick look at the total outstanding balances and due dates. When a company receives goods or which accounts are found on an income statement services but has yet to pay, it logs the amount owed as an AP entry. Typically, this involves the date of the transaction, the amount due, and the payment deadline. Accounts receivable affects your cash flow regardless of whether you use the cash or accrual method, because you cannot spend money that you have not yet received. In addition, if you use the accrual method and you have taxes due on income or sales amounts for which you have not yet been paid, then your cash flow will be further impacted by having to pay taxes on these sums.
What is the accounts receivable turnover ratio?
- Whether cash payment was received or not, revenue is still recognized on the income statement and the amount to be paid by the customer can be found on the accounts receivable line item.
- When a company sells its products or services, it may not receive money in exchange simultaneously.
- However, the manufacturer is a long-time customer with an agreement that provides them with 60 days to pay post-receipt of the invoice.
- It may be obvious intuitively, but, by definition, a cash sale cannot become a bad debt, assuming that the cash payment did not entail counterfeit currency.
- The understanding is that the couple will make payments each month toward the principal borrowed, plus interest.
- This is different from the last journal entry, where bad debt was estimated at $58,097.
For example, a category might consist of accounts receivable that is 0–30 days past due and is assigned an uncollectible percentage of 6%. Another category might be 31–60 days past due and is assigned an uncollectible percentage of 15%. All categories of estimated uncollectible amounts are summed to get a total estimated uncollectible balance.
Accounts payable and accounts receivable have distinct impacts on a business’s cash flow. Accounts payable (AP) signifies cash outflows since a company needs to make payments to suppliers, directly reducing available cash. The following https://x.com/bookstimeinc table reflects how the relationship would be reflected in the current (short-term) section of the company’s Balance Sheet. The first entry reverses the bad debt write-off by increasing Accounts Receivable (debit) and decreasing Bad Debt Expense (credit) for the amount recovered. The second entry records the payment in full with Cash increasing (debit) and Accounts Receivable decreasing (credit) for the amount received of $15,000. For the taxpayer, this means that if a company sells an item on credit in October 2018 and determines that it is uncollectible in June 2019, it must show the effects of the bad debt when it files its 2019 tax return.
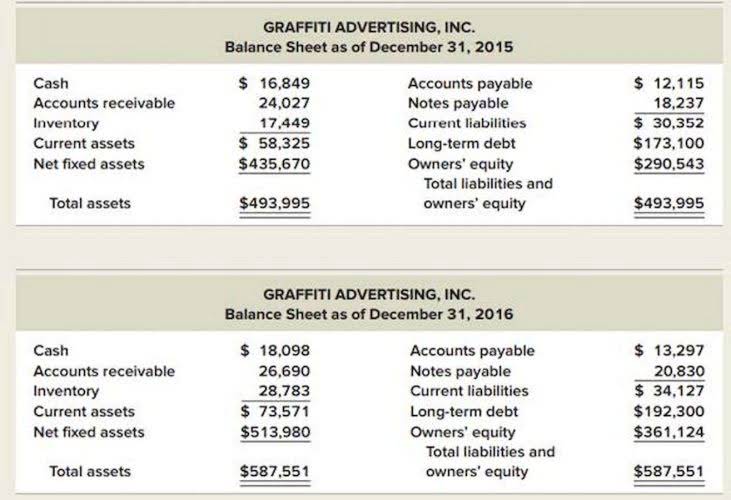
Simple Balance Sheet Template
An accounting journal is an accounting worksheet that allows you to track each of the steps of the accounting process, side by side. This accounting journal template includes each step with sections for their debits and credits, and pre-built formulas to calculate the total balances for each column. One of the fundamental differences between accounts payable and accounts receivable lies in their placement on the financial statements. As you’ve learned, the delayed recognition of bad debt violates GAAP, specifically the matching principle.
Tips for improving A/R management
Hence, the income statement is delaying the reporting of bad debts expense on its income statement until an account receivable is actually written off as uncollectible. The balance sheet aging of receivables method estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable, but it also considers the uncollectible time period for each account. The longer the time passes with a receivable unpaid, the lower the probability that it will get collected. An account that is 90 days overdue is more likely to be unpaid than an account that is 30 days past due.

These resources can result in inflows of economic benefits in the future. Accounts receivable is crucial in reporting a company’s assets under the accrual concept. Usually, it goes against the cash method for accounting which only recognizes cash transactions.

